Healthy gums are more than just a pretty smile for your feline friend; they are a crucial indicator of their overall well-being. Just like humans, a cat’s oral health is intrinsically linked to their systemic health. Examining your cat’s gums regularly can provide vital clues about everything from hydration levels to potential underlying diseases. Understanding what healthy cat gums look like, and more importantly, recognizing the warning signs of unhealthy gums, empowers you to take proactive steps in ensuring your kitty stays happy and healthy. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about healthy cat gums and how to use a Cat Gum Color Chart to monitor your feline companion’s health effectively.
Decoding Healthy Cat Gums: What is Normal?
During a routine veterinary check-up, one of the first things your vet will do is examine your cat’s mouth. A quick peek at your cat’s gums provides a wealth of information. Healthy gums are a sign of good oral hygiene and can also reflect a healthy circulatory system, adequate hydration, and the absence of certain systemic diseases. But what exactly should you be looking for when assessing your cat’s gums at home?
Healthy cat gums typically exhibit the following characteristics:
- Color: The ideal color for healthy cat gums is often described as salmon pink. This indicates good blood flow and oxygenation.
- Moisture: Healthy gums should be moist, not dry or sticky. Moisture is a good indicator of proper hydration.
- Capillary Refill Time (CRT): This is a simple yet informative test you can perform at home. Gently press on your cat’s gums with your finger. The spot you pressed will briefly turn paler than the surrounding gum tissue. Release the pressure and observe how quickly the pink color returns. In a healthy cat, the color should return to normal in under two seconds. This is known as the capillary refill time and it provides insights into your cat’s blood circulation and cardiovascular health.
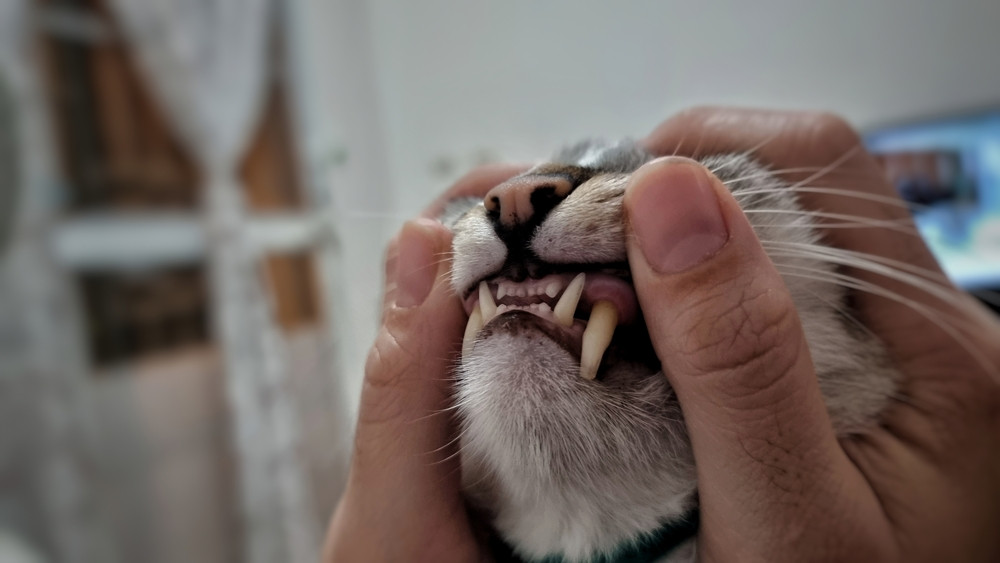 A close-up of healthy pink cat gums, showing the ideal color and moisture.
A close-up of healthy pink cat gums, showing the ideal color and moisture.
It’s also important to note that some cats may have small, harmless black spots or patches on their gums. This pigmentation, called lentigo simplex, is similar to freckles in humans and is a benign condition that requires no treatment. These spots are flat and should not be raised or cause any discomfort to your cat.
Regular Gum Checks: Monitoring Your Cat’s Oral Health at Home
For healthy adult cats, a weekly gum check is a good practice to establish. This allows you to become familiar with your cat’s normal gum appearance and quickly identify any changes that may arise. If your cat is older, has a history of dental problems, or is currently unwell, you might want to increase the frequency of gum checks to daily to closely monitor for any fluctuations.
Making gum checks a routine part of your cat care is easier than you might think. You can incorporate it into cuddle time or grooming sessions. Gently lift your cat’s lip to expose their gums. Observe the color, moisture, and check for any unusual swelling or lesions. Practice the capillary refill time test periodically to ensure you are familiar with your cat’s baseline.
Warning Signs: When Cat Gums Signal a Problem
While healthy gums are pink and moist, any deviation from this norm should be considered a potential warning sign. Changes in your cat’s gum appearance can indicate a range of issues, from mild dental problems to serious systemic diseases. It’s crucial to be vigilant and know what to look for. Contact your veterinarian promptly if you observe any of the following changes in your cat’s gums:
- Color Changes: Any change from the normal salmon pink color is significant. We will delve into the specifics of different gum colors and their meanings in the cat gum color chart section below.
- Dryness: Dry or sticky gums are a sign of dehydration. Dehydration can be caused by various factors, including insufficient water intake, fever, vomiting, or diarrhea. Dehydration is a serious concern and requires veterinary attention.
- Inflammation (Gingivitis): Red, swollen, or inflamed gums, especially along the gumline where the gums meet the teeth, are a hallmark of gingivitis. This is an early stage of dental disease caused by plaque and bacteria buildup. Inflamed gums may also bleed easily when touched.
- Lesions, Growths, or Masses: Any raised tissue, sores, ulcers, injuries, or unusual lumps on the gums should be examined by a veterinarian. These could be indicative of infection, injury, or even oral tumors.
- Gum Overgrowth: If the gums appear to be growing over the teeth, this could be gingival hyperplasia. This condition can be caused by chronic inflammation, certain medications, or breed predisposition and needs veterinary evaluation.
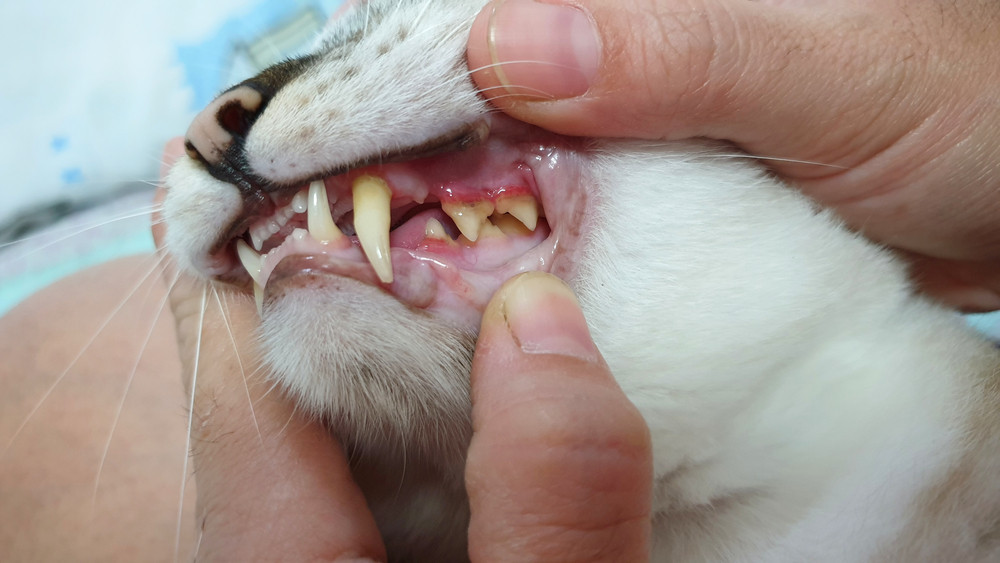 Inflamed and red cat gums, indicating gingivitis and potential dental disease.
Inflamed and red cat gums, indicating gingivitis and potential dental disease.
The Cat Gum Color Chart: A Guide to Interpretation
The color of your cat’s gums is a surprisingly informative indicator of their health. Different colors can signal various underlying conditions, some of which require immediate veterinary intervention. This cat gum color chart serves as a quick reference guide to help you understand what different gum colors might mean:
| Gum Color | Possible Meaning | Action to Take |
|---|---|---|
| Pink (Salmon Pink) | Normal, Healthy Gums. Indicates good circulation and oxygenation. | No action needed. Continue routine monitoring. |
| Pale Pink or White | Anemia, Low Blood Pressure. Could indicate blood loss, shock, or underlying conditions like kidney disease or internal parasites. | Contact your veterinarian IMMEDIATELY, especially if your cat is also lethargic, weak, or has pale mucous membranes (like inside the eyelids). This can be an emergency. |
| Bright Red (Gum Margin) | Gingivitis. Inflammation of the gums, often the first sign of dental disease. Caused by plaque and tartar buildup. | Schedule a dental checkup with your veterinarian. Early intervention can prevent progression to more severe periodontal disease. |
| Bright Red (Entire Gumline) | Heatstroke, Allergic Reaction, Sepsis. Widespread redness can indicate systemic inflammation or a body-wide reaction. | Seek EMERGENCY veterinary care. These conditions are serious and require immediate treatment. Cool your cat down if heatstroke is suspected while en route to the vet. |
| Brick Red or Brown | Toxicity, Methemoglobinemia. Could indicate ingestion of toxins (like acetaminophen/paracetamol) or certain blood disorders. | Contact your veterinarian IMMEDIATELY. Bring any suspected toxins with you to the vet. |
| Yellow (Jaundice) | Jaundice, Liver or Gallbladder Issues, Hemolytic Anemia. Yellow gums (and often yellowing of the whites of the eyes and skin) indicate elevated bilirubin levels, often due to liver problems or red blood cell destruction. | Schedule a veterinary exam for bloodwork and diagnostics. Jaundice is a serious sign of underlying disease that needs to be diagnosed and treated. |
| Blue, Purple, or Gray | Cyanosis, Low Blood Oxygen. Indicates insufficient oxygen in the blood, potentially due to respiratory distress, heart failure, or airway obstruction. | Seek EMERGENCY veterinary care. Cyanosis is a life-threatening emergency. Ensure your cat has a clear airway and transport them to the nearest emergency vet clinic immediately. |
| Black | Normal Pigmentation (in some cats). Often normal in cats with dark skin or pigmented gums. Raised Black Spots: Potential Oral Mass. Raised or growing black spots are concerning. | If flat and not raised, likely normal. If raised or changing, schedule a veterinary exam for evaluation. Oral masses, including melanomas, can occur in cats and require diagnosis and treatment. |
Important Note: This cat gum color chart is intended as a guide for pet owners. It is not a substitute for professional veterinary diagnosis. If you notice any abnormal gum color or other concerning signs, always consult with your veterinarian for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Root Causes of Unhealthy Cat Gums
Many factors can contribute to unhealthy gums in cats, ranging from poor oral hygiene to underlying systemic illnesses. Understanding these causes can help you take preventative measures and recognize potential problems early.
- Dental Disease: The most common culprit behind unhealthy gums is dental disease. Plaque and tartar accumulation lead to bacterial overgrowth in the mouth, causing gingivitis (gum inflammation) and periodontitis (inflammation of the tissues surrounding the teeth). Without regular dental care, dental disease is almost inevitable in cats.
 Cat teeth with tartar buildup, a common cause of dental disease and gum problems.
Cat teeth with tartar buildup, a common cause of dental disease and gum problems.
- Genetics and Breed Predisposition: Some cat breeds are genetically predisposed to developing dental disease, making them more susceptible to gum problems. Breeds like Persians, Himalayans, and Siamese, with their brachycephalic or specific genetic lines, may be at higher risk.
- Underlying Systemic Illnesses: Certain systemic diseases can increase the risk of dental disease and negatively impact gum health. These include:
- Kidney Disease: Cats with kidney disease are prone to developing oral ulcers and stomatitis, which can affect the gums.
- Diabetes Mellitus: Diabetic cats are more susceptible to infections, including gum infections.
- Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV) and Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV): These viruses weaken the immune system, making cats more vulnerable to dental disease and gum infections.
- Oral Tumors: While less common, oral tumors can also affect the gums, causing swelling, lesions, and discoloration.
Why Healthy Gums are Essential for Your Cat’s Well-being
Healthy gums are not just about a pretty smile; they are fundamental to your cat’s overall health and comfort. Ignoring gum health can have significant consequences:
- Pain and Discomfort: Gingivitis and periodontal disease are painful conditions. Inflamed gums are sensitive, making eating uncomfortable and affecting your cat’s quality of life.
- Tooth Loss and Infection: Untreated dental disease progresses, leading to gum recession, bone loss around the teeth, tooth decay, and ultimately tooth loss. Severe dental infections can also spread to other parts of the body.
- Systemic Health Impact: The mouth is a gateway to the body. Bacteria from severe dental disease can enter the bloodstream and potentially affect major organs like the heart, kidneys, and liver. Dental issues have even been linked to cognitive dysfunction in older cats.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Painful dental conditions can make eating difficult, leading to reduced food intake, weight loss, and nutritional deficiencies.
 A happy and healthy cat, emphasizing the importance of overall well-being, including dental health.
A happy and healthy cat, emphasizing the importance of overall well-being, including dental health.
What to Do If You Suspect Unhealthy Gums
Early detection and intervention are key when it comes to cat gum health. If you notice any changes in your cat’s gum color, moisture, or appearance, or if you suspect any dental problems, schedule a veterinary appointment promptly.
Do not attempt home treatment for significant gum issues, especially if your cat is showing signs of illness like lethargy, loss of appetite, vomiting, or difficulty breathing. Conditions indicated by pale, bright red, yellow, or blue gums are particularly urgent and require immediate veterinary attention.
Proactive Steps to Maintain Healthy Cat Gums
Prevention is always better than cure. Maintaining healthy cat gums involves a combination of professional veterinary care and consistent at-home dental hygiene practices.
-
Regular Veterinary Dental Checkups and Professional Cleanings: Annual veterinary checkups should include a thorough oral exam. Your veterinarian will recommend professional dental cleanings under anesthesia as needed to remove plaque and tartar buildup below the gumline.
-
Daily Home Dental Care: Consistent at-home dental hygiene is crucial in preventing dental disease and maintaining healthy gums. Effective methods include:
-
Daily Tooth Brushing: The gold standard for home dental care is daily tooth brushing using a pet-safe enzymatic toothpaste. Never use human toothpaste, as it contains ingredients that are toxic to cats.
-
VOHC-Approved Water Additives: Veterinary Oral Health Council (VOHC) approved water additives can help reduce plaque and tartar buildup when added to your cat’s drinking water.
 VOHC-approved water additive for cats, a convenient way to support dental health.
VOHC-approved water additive for cats, a convenient way to support dental health.- Dental Treats and Chews: Certain dental treats and chews are formulated to help reduce plaque and tartar. Look for VOHC-approved dental treats for proven effectiveness.
 VOHC-approved dental treats for cats, a palatable way to aid in dental cleaning.
VOHC-approved dental treats for cats, a palatable way to aid in dental cleaning.- Dental Wipes: Dental wipes can be used to gently clean your cat’s teeth and gums, especially for cats who are resistant to brushing.
 Dental wipes for cats, a gentle alternative for cleaning teeth and gums.
Dental wipes for cats, a gentle alternative for cleaning teeth and gums.- Breath Fresheners with Dental Benefits: Some breath fresheners are designed to also promote dental health by reducing bacteria in the mouth.
 Breath freshener for cats with dental benefits, helping to freshen breath and support oral hygiene.
Breath freshener for cats with dental benefits, helping to freshen breath and support oral hygiene.- Dental Diets: Dental-specific cat food diets are formulated with larger kibble size and textures that help to scrape teeth clean as your cat eats.
 Dental diet cat food, formulated to help clean teeth while chewing.
Dental diet cat food, formulated to help clean teeth while chewing.- Prescription Dental Diets: For cats with significant dental disease, your veterinarian may prescribe specific prescription dental diets that offer enhanced dental benefits.
 Prescription dental diet cat food, often recommended for cats with existing dental issues.
Prescription dental diet cat food, often recommended for cats with existing dental issues. -
-
Overall Health Management: Maintaining your cat’s overall health through proper nutrition, regular veterinary checkups, and prompt treatment of any systemic illnesses also contributes to healthy gums. Routine bloodwork and urinalysis can help detect early signs of conditions like kidney or liver disease that can impact oral health.
Conclusion: Healthy Gums, Happy Cat
Paying attention to your cat’s gum health is an integral part of responsible cat ownership. By understanding what healthy gums look like, recognizing warning signs, and using the cat gum color chart as a guide, you can proactively monitor your feline friend’s oral health. Combined with regular veterinary care and consistent at-home dental hygiene, you can help ensure your cat enjoys a healthy, pain-free mouth and a happier, healthier life. Don’t hesitate to reach out to your veterinarian if you have any concerns about your cat’s gum health. Your cat’s well-being is always worth it.

