While we often look to a cat’s eyes for clues to their emotions, their tail movements offer a wealth of information about how they are feeling. Just like dogs, cats use their tails to communicate, and understanding this “cat tail language,” especially the nuances of a Cat Wagging Tail, is key to deepening your bond with your furry friend.
Why Understanding Cat Tail Wagging Matters
Learning to interpret your cat wagging tail and overall body language allows you to better understand your cat’s emotional state during different interactions. This knowledge helps you identify situations and environments that bring your cat joy or trigger fear and anxiety. Recognizing the subtle cues of a cat wagging tail can also be an invaluable tool in identifying potential illness or pain in your feline companion, enabling you to seek timely veterinary care.
A Comprehensive Guide to Cat Tail Language, Including the Wag
These insights into cat tail language will empower you to foster a more loving, trusting, and enriching relationship with your cat. Let’s delve into the various positions and movements, focusing particularly on what a cat wagging tail truly signifies.
The Upright Tail: Confidence and Sociability
 Illustration of a happy cat holding their tail straight up
Illustration of a happy cat holding their tail straight up
When a cat holds their tail straight up, it’s a clear sign of confidence and sociability. This upright posture indicates they are feeling friendly and are approaching you or other animals in a welcoming manner.
This tail position is a common greeting among cats, and it’s also how kittens greet their mothers. A 1997 study from the University of Southampton highlighted this, showing that cats were more likely to approach a cat-shaped silhouette with a raised tail compared to one with a lowered tail.
If your cat approaches you with an upright tail, it’s an invitation for interaction. This is an ideal moment to offer petting or engage in playtime.
The Question Mark Tail: Playful Invitation
 Illustration of a cat with a question mark tail
Illustration of a cat with a question mark tail
Sometimes, you might notice your cat’s tail forming a question mark shape – upright with a curl at the tip. This cat wagging tail variation also signifies happiness and a friendly approach.
A question mark tail is your cat’s way of inviting interaction. While the curled tip might be tempting to touch, remember that cats generally prefer being petted around their facial glands, located on their cheeks, under their chin, and near their ears.
The Low-Hanging Tail: Fear or Anxiety
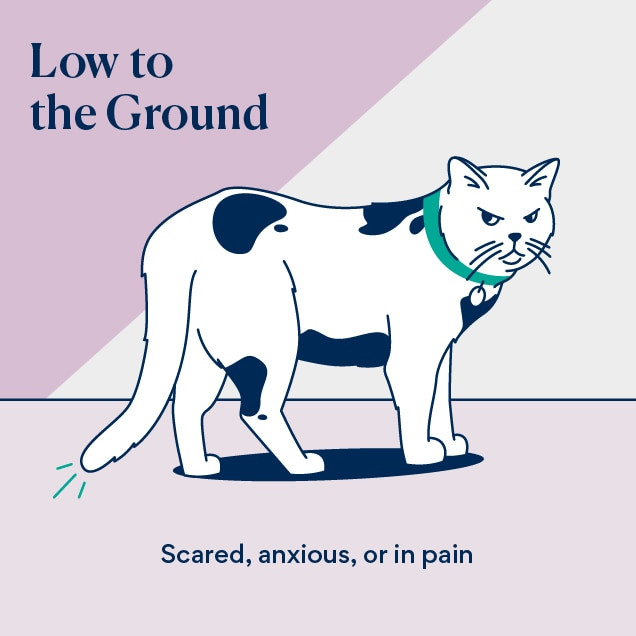 Illustration of cat tail language of a tail held low to the ground indicating fear or anxiety
Illustration of cat tail language of a tail held low to the ground indicating fear or anxiety
A tail held low, below the level of their back, often indicates that a cat is feeling frightened or anxious. If the tail is tucked tightly between their legs, it signals a higher level of fear or even potential pain.
The Puffed-Up Tail: Startled and Defensive
 Illustration of a cat with a puffed-up tail indicating fear or defensiveness
Illustration of a cat with a puffed-up tail indicating fear or defensiveness
The classic Halloween cat posture, featuring a puffed-up tail and arched back, is a sign of a startled or frightened cat facing a sudden, perceived threat.
The hair standing on end, known as piloerection, is a defense mechanism to make the cat appear larger and more intimidating. This posture is a clear indication that your cat wants to be left alone. Common triggers include unfamiliar animals in the yard, approaching dogs, visitors, or loud, sudden noises.
To alleviate your cat’s stress, it’s crucial to remove the source of their fear. Approaching a cat in this state can be misinterpreted as a further threat, potentially leading to aggression.
The Wrapped Tail: Fear, Pain, or Illness
 Illustration of cat tail language when a cat wraps their tail around their body indicating fear or discomfort
Illustration of cat tail language when a cat wraps their tail around their body indicating fear or discomfort
When a cat sits or lies down with their tail wrapped closely around their body, it’s usually a sign of fear, defensiveness, pain, or general unwellness. If you observe this posture, it’s best to cease interaction and ensure their environment is calm and stress-free.
Persistent crouching with a tightly curled tail for more than a couple of days warrants a veterinary check-up to rule out any underlying pain or illness.
Decoding the Wag: Different Types of Cat Wagging Tail Movements
Similar to dogs, cats utilize tail movements, including the cat wagging tail, to express a spectrum of emotions. However, unlike the often enthusiastic tail wags of dogs, a cat wagging tail can have varied and sometimes contradictory meanings. It’s vital to understand the different types of “wags” to accurately interpret your cat’s feelings.
Thrashing Tail: Irritation or Anger
 Illustration of a cat thrashing their tail indicating irritation or anger
Illustration of a cat thrashing their tail indicating irritation or anger
When a cat thrashes their tail from side to side or thumps it forcefully on the ground, it’s a clear indication of irritation, annoyance, or anger. This vigorous cat wagging tail motion signals that something is bothering your feline friend.
This behavior is a “distance-increasing” signal. For instance, if you are petting your cat and they begin thrashing their tail, they are communicating that they want you to stop. Ignoring this warning cat wagging tail can escalate into hissing, growling, swatting, or even biting.
Twitching Tail Tip: Focused Attention or Mild Annoyance
 Illustration of cat tail language when a cat is twitching their tail indicating focus or mild irritation
Illustration of cat tail language when a cat is twitching their tail indicating focus or mild irritation
Cats often twitch just the end of their tails when they are in a state of focused attention, such as during hunting or play, or when they are experiencing mild irritation or frustration. Context is crucial here. If they aren’t engaged in play or stalking prey, a twitching cat wagging tail likely signifies mild annoyance. Observe the surrounding situation and other body language cues to accurately gauge their mood.
Swishing Tail: Intense Focus and Predatory Mode
 Cat tail language illustration of a cat swishing their tail indicating focus or predatory intent
Cat tail language illustration of a cat swishing their tail indicating focus or predatory intent
A slow, deliberate swishing of the tail from side to side often indicates intense focus. Your cat might be concentrating on a toy, another pet, or something outside that has captured their attention. This type of cat wagging tail movement often precedes pouncing or other predatory behaviors.
Allowing your cat to engage in these stalking and pouncing behaviors is beneficial for their enrichment. Let them continue to focus on whatever has captivated them, providing a healthy outlet for their natural instincts.
Quivering Tail: Excitement or Marking Behavior
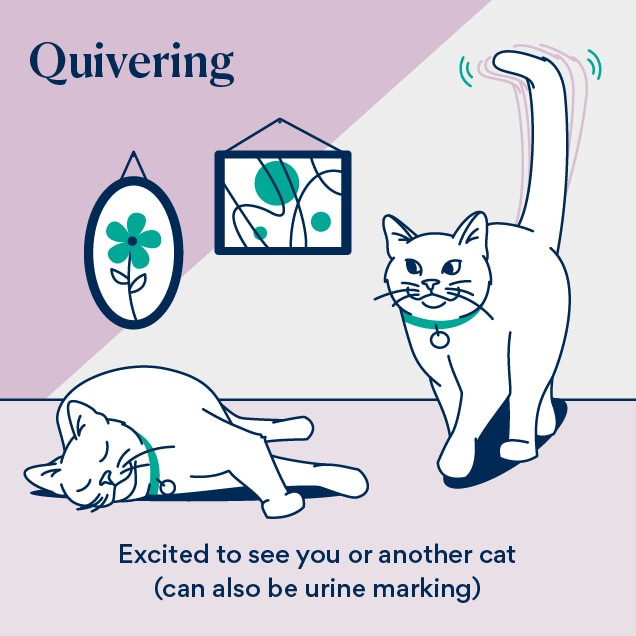 Illustration of a cat tail illustration of a quivering tail indicating excitement or urine marking
Illustration of a cat tail illustration of a quivering tail indicating excitement or urine marking
A quivering tail often expresses excitement, especially when greeting you or another familiar cat. However, it’s important to note that a quivering tail, held straight up while the cat backs up against a vertical surface, can also indicate urine marking, a territorial behavior.
The Affectionate Tail Wrap: Bonding and Greeting
 Illustration of cat tail language when a cat wraps their tail around human legs indicating affection
Illustration of cat tail language when a cat wraps their tail around human legs indicating affection
Just as humans use handshakes or hugs, cats use tail wrapping as a friendly greeting. They may curl their tails around your legs or intertwine tails with other cats as a sign of affiliation and a willingness to interact.
While understanding cat wagging tail and other tail movements is crucial, remember to consider the entire picture of your cat’s body language to fully grasp their emotional state. The tail, however, remains one of the most expressive indicators of feline feelings. By learning to interpret these subtle cues, you can significantly strengthen your bond and communication with your beloved cat.
WRITTEN BY
Alison Gerken, DVM (Clinical Behavior Resident)Veterinarian
Dr. Alison Gerken is a second-year resident in veterinary behavior at the Florida Veterinary Behavior Service under the mentorship of…
