Do you wonder, “What Does A Cat Wagging His Tail Mean?” The answer is multifaceted, and understanding it enhances your bond with your feline friend. At solcat.net, we help you decipher your cat’s tail wags and other behaviors.
1. Why It’s Crucial to Understand What Cat Tail Wagging Means
Decoding your cat’s tail signals is vital for a harmonious relationship. Understanding your cat’s body language helps determine how your kitty feels about particular interactions. This allows you to identify the situations or environments that make your cat happy or cause fear. Reading the tail language of a cat can also help you identify illness and pain more readily. By learning what different tail movements signify, you can better respond to their needs, creating a happier and healthier environment for them. This knowledge not only strengthens your connection but also aids in recognizing potential health issues early on, contributing to your cat’s overall well-being.
2. Understanding Your Cat’s Tail Language
These tips for understanding cat tail language will empower you to build a more loving, trusting, and fulfilling relationship with your cat. A cat’s tail is like a flag signaling their emotional state. By observing the position and movement of their tail, you can gain valuable insights into their mood, intentions, and overall well-being. This knowledge will help you respond appropriately and strengthen your connection with your feline companion.
2.1. Your Cat’s Tail Is Straight Up
When a cat’s tail is upright, they are feeling social and confident, and are approaching in a friendly manner. An upright tail signifies confidence, happiness, and a willingness to interact. This position is often accompanied by a friendly approach, indicating that your cat is in a positive and receptive mood.
 illustration of a happy cat holding their tail straight up
illustration of a happy cat holding their tail straight up
This cat tail language indicates a friendly greeting between cats, and it’s how kittens greet their mothers. A 1997 study by the University of Southampton found that cats were willing to readily approach a cat-shaped silhouette if it had a raised tail but were reluctant to approach the silhouette if it had a lowered tail.
If your cat approaches you with their tail up, they are open to an interaction. This is a good time to pet them or play with them. If your cat approaches you with their tail held high, it’s an invitation to engage. This gesture signifies their openness to affection and play. Take this opportunity to shower them with attention, whether it’s through gentle petting or an engaging play session.
2.2. Your Cat’s Tail Is a Question Mark or Hook
You may notice that sometimes your cat’s tail looks like a question mark—it stands upright but curls at the end. Again, this cat tail language indicates that your cat is happy and approaching amicably. A tail resembling a question mark suggests playfulness and curiosity.
 illustration of a cat
illustration of a cat
When your cat’s tail is in this position, it means it’s an invitation to interact with your cat. However, while it is tempting to pet that curly-tipped tail, most cats prefer to be pet around their facial glands on their cheeks, under their chin, and next to their ears. When your cat displays this tail posture, it’s an indication that they’re in the mood for interaction. While the curly-tipped tail may be tempting to touch, most cats prefer being petted around their facial glands, such as their cheeks, under their chin, and next to their ears. Understanding and respecting their preferred petting spots can enhance your bond and make interactions more enjoyable for both of you.
2.3. Your Cat’s Tail Is Held Low to the Ground
A cat may lower their tail below the level of their back if they are frightened or anxious. If your cat’s tail is tucked between their legs, then they are really scared or may be experiencing pain. A low-hanging tail signals fear, anxiety, or submission. This position indicates discomfort or a desire to avoid confrontation.
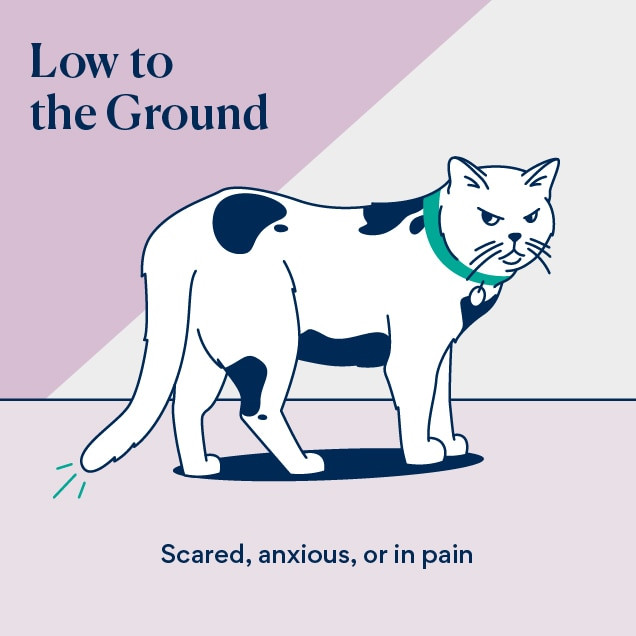 illustration of cat tail language of a tail held low to the ground
illustration of cat tail language of a tail held low to the ground
2.4. Your Cat’s Tail Is Puffed Up
If your cat assumes the quintessential Halloween-cat posture with a puffed tail and arched back, then they are startled or frightened by a sudden, severe threat. A puffed-up tail is a clear sign of fear or aggression. The cat is trying to appear larger to ward off a perceived threat.
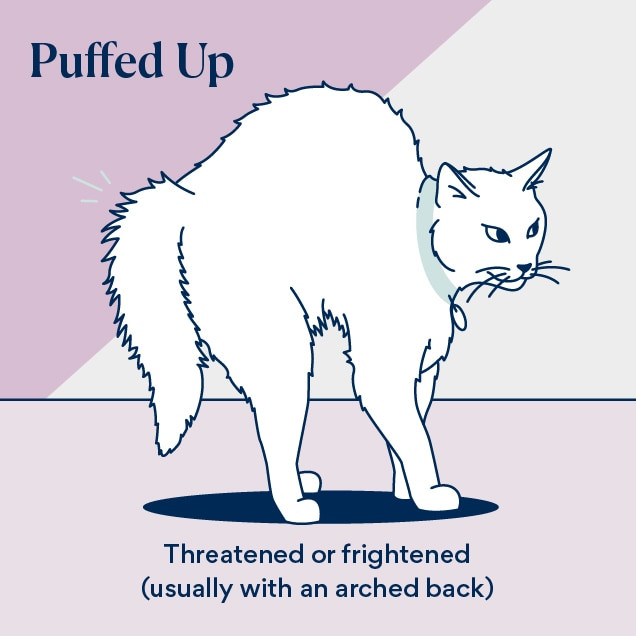 illustration of a cat
illustration of a cat
Your cat’s hair stands on end (piloerection) so they can appear to be larger. This is a defensive reaction indicating that your cat wishes to be left alone. This tail position is often triggered by feeling threatened, such as by other animals in the yard, approaching dogs, visitors in the home, or sudden noises.
Remove the inciting triggers to decrease your cat’s stress. If you try to interact with your cat when their hair is standing up, they may perceive your approach as a threat and become aggressive. It’s crucial to avoid approaching or interacting with your cat when their hair is standing up, as they may perceive your presence as a threat and react aggressively. Instead, focus on identifying and removing any triggers that may be causing them stress, such as other animals in the yard, approaching dogs, visitors in the home, or sudden noises. By creating a calm and safe environment, you can help alleviate your cat’s anxiety and prevent potential conflicts.
2.5. Your Cat’s Tail Is Wrapped Around Their Body
If your cat is sitting or lying down with their tail wrapped around their body, then they are frightened, defensive, in pain, or feeling unwell. When you see this, end your interaction with your cat and ensure that your cat’s environment is free of stressors. A tail wrapped around the body indicates fear, defensiveness, or discomfort.
 illustration of cat tail language when a cat
illustration of cat tail language when a cat
If your cat frequently crouches with their tail curled tightly around their body for more than a few days, then an evaluation by your veterinarian is warranted to rule out pain or illness. If your cat frequently exhibits this posture for more than a few days, it’s essential to seek veterinary attention to rule out any underlying health issues or sources of pain. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve your cat’s quality of life and overall well-being.
3. Understanding “What Does It Mean When A Cat Wags Its Tail?”
Just like dogs, cats move their tail to express their emotions. But not all wag-like motions are the same—many cat tail movements convey completely different meanings. Decoding the subtle nuances of a cat’s tail wags can provide valuable insights into their emotional state. While a wagging tail in dogs often signifies happiness, in cats, it can indicate a range of emotions, from annoyance to excitement. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurately interpreting your cat’s behavior and responding appropriately.
So, what does it mean when a cat wags its tail? Let’s take a look at the different “wagging” tail movements and what they mean. By observing the speed, intensity, and accompanying body language, you can gain a deeper understanding of what your feline friend is trying to communicate.
3.1. Thrashing Tail Movements
When your cat thrashes their tail or is thumping it on the ground, they are irritated, annoyed, or angry. This tells you that something is bothering your cat. When a cat’s tail thrashes or thumps against the ground, it’s a clear indication of irritation, annoyance, or anger. This behavior signals that something is bothering your cat, and it’s essential to identify and address the cause of their distress.
 illustration of a cat trashing their tail
illustration of a cat trashing their tail
This is a distance-increasing behavior. In other words, if you are petting your cat and they start thrashing their tail, they are trying to tell you to stop. If you don’t, then the thrashing tail may be a prelude to hissing, growling, swatting, or biting. When you observe your cat thrashing their tail, it’s crucial to respect their boundaries and avoid any further interaction that may escalate their agitation. Ignoring these warning signs may lead to hissing, growling, swatting, or even biting, as your cat attempts to communicate their discomfort more forcefully.
3.2. Twitching the End of the Tail
Cats twitch the end of their tails when they are hunting and playing, as well as when they are mildly irritated and frustrated. In this case, read the scene and look for other clues to their mood. If they’re not playing or stalking something, then the twitching tail movement probably means that they are annoyed. A twitching tail can indicate excitement, focus, or mild irritation. Context is key to understanding the underlying emotion.
 illustration of cat tail language when a cat is twitching their tail
illustration of cat tail language when a cat is twitching their tail
3.3. Swishing Tails
When your cat slowly swishes their tail from side to side, they may be intently focused on something like a toy, another animal in the home, or something outside. They may be about to pounce! A slow, deliberate swish often indicates focus and anticipation, especially when stalking prey.
 cat tail language illustration of a cat swishing their tail
cat tail language illustration of a cat swishing their tail
Engaging in predatory behavior like stalking and pouncing is good enrichment for your cat, so let them continue to engage in whatever is captivating their attention. Allow your cat to continue engaging in these activities, as they provide valuable mental and physical stimulation, contributing to their overall well-being and happiness.
3.4. Tail Quivers
Your cat may quiver their tail when they are especially excited to see you or another cat. Though, sometimes, when a cat quivers their tail while holding it straight up and backing up against a vertical surface, they may be urine marking. A quivering tail can signify excitement or, in some cases, urine marking. Observing the accompanying body language is crucial for accurate interpretation.
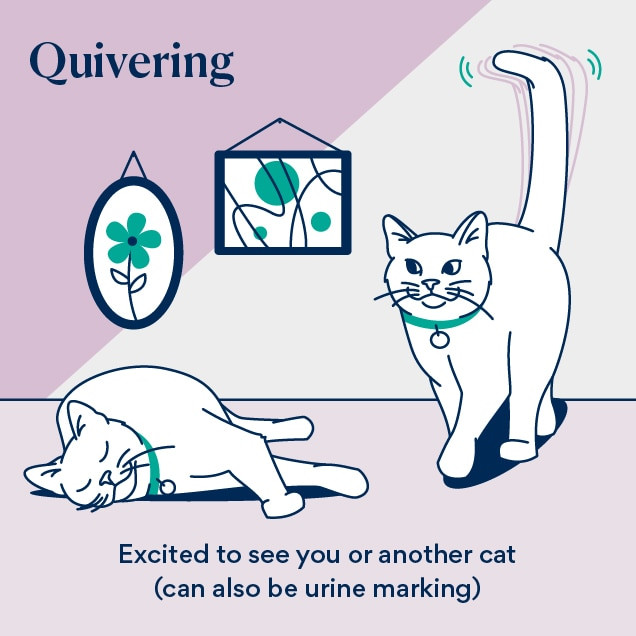 illustration of a cat tail illustration of a quivering tail
illustration of a cat tail illustration of a quivering tail
4. Why Do Cats Wrap Their Tails Around You?
Just as we greet one another with handshakes or hugs, cats may greet by curling their tails around people and by intertwining their tails with other cats. Tail wrapping is an affiliative behavior that demonstrates a willingness to interact. When a cat wraps its tail around you, it’s a sign of affection and trust. This gesture indicates that your cat feels comfortable and secure in your presence, viewing you as a member of their social group.
 illustration of cat tail language when a cat wraps their tail around human legs
illustration of cat tail language when a cat wraps their tail around human legs
Although you should look at more than just their tail movements, to fully understand your cat’s emotional state, the tail may be the most expressive part of a cat’s body language. Better understanding your cat’s body language will surely improve your bond with your cat. By paying attention to their tail movements and other body language cues, you can gain valuable insights into their emotional state and respond accordingly. This, in turn, strengthens your bond and enhances your ability to provide them with the care and attention they need.
5. Additional Factors Influencing Cat Tail Wagging
Several other factors can influence a cat’s tail wagging behavior, including breed, age, and individual personality. Some breeds may be more prone to certain tail movements, while kittens may exhibit different tail signals than adult cats. Additionally, each cat has its unique personality and communication style, which can impact how they use their tail to express themselves.
5.1. Environmental Factors
The environment in which a cat finds itself can also play a significant role in their tail wagging behavior. Changes in the environment, such as the introduction of a new pet or rearranging furniture, can cause stress or anxiety, leading to changes in tail movements. Loud noises or unfamiliar scents can also trigger specific tail responses.
5.2. Health Conditions
In some cases, changes in a cat’s tail wagging behavior may be indicative of underlying health conditions. For example, nerve damage or arthritis in the tail can cause unusual movements or sensitivity. If you notice any sudden or unexplained changes in your cat’s tail behavior, it’s essential to consult with a veterinarian to rule out any potential medical issues.
5.3. The Role of Scent
Cats also use their tails to spread their scent, which plays a crucial role in communication. When a cat rubs its tail against objects or people, it’s depositing pheromones that convey information about its identity, social status, and emotional state. This scent marking behavior can influence how other cats perceive and interact with the marking cat.
6. The Importance of Observing Other Body Language Cues
While tail wagging provides valuable insights into a cat’s emotional state, it’s essential to consider other body language cues for a more complete understanding. Facial expressions, ear positions, body posture, and vocalizations all contribute to the overall message a cat is conveying.
6.1. Facial Expressions
A cat’s facial expressions can reveal a wealth of information about its mood and intentions. Dilated pupils may indicate fear or excitement, while narrowed eyes can signal aggression or discomfort. The position of the whiskers can also provide clues, with forward-pointing whiskers suggesting curiosity and flattened whiskers indicating anxiety.
6.2. Ear Positions
The position of a cat’s ears can also be indicative of its emotional state. Forward-pointing ears typically signify alertness and interest, while flattened ears may indicate fear or aggression. Swiveling ears suggest that the cat is actively listening and processing information from its surroundings.
6.3. Body Posture
A cat’s body posture can reveal whether it’s feeling confident, threatened, or submissive. A cat that stands tall with its back arched and fur raised is trying to appear larger and more intimidating. Conversely, a cat that crouches low to the ground with its tail tucked between its legs is signaling fear or submission.
6.4. Vocalizations
Cats use a variety of vocalizations to communicate, including meows, purrs, hisses, and growls. Each vocalization conveys a different message, ranging from a friendly greeting to a warning of impending aggression. By paying attention to the context and accompanying body language, you can better understand the meaning behind a cat’s vocalizations.
7. Common Misconceptions About Cat Tail Wagging
There are several common misconceptions about cat tail wagging that can lead to misinterpretations of their behavior. One of the most prevalent myths is that a wagging tail always indicates happiness, as it often does in dogs. However, as we’ve discussed, a cat’s tail wag can signify a range of emotions, including annoyance, frustration, or even aggression.
7.1. All Wags Are the Same
Another misconception is that all wags are the same. The speed, intensity, and direction of the wag can all provide valuable clues about the cat’s emotional state. A slow, deliberate wag may indicate focus or anticipation, while a rapid, erratic wag can signal agitation or fear.
7.2. Ignoring Context
Ignoring the context in which the tail wagging occurs is another common mistake. A twitching tail may indicate excitement during playtime but could signify irritation if the cat is being petted excessively. Considering the surrounding circumstances and other body language cues is essential for accurate interpretation.
8. How to Respond to Different Cat Tail Signals
Knowing how to respond to different cat tail signals is crucial for maintaining a positive and harmonious relationship with your feline companion. If your cat is displaying signs of fear or anxiety, it’s essential to provide a safe and calming environment. Avoid forcing interaction and allow your cat to retreat to a quiet space where it feels secure.
8.1. Respecting Boundaries
If your cat is signaling annoyance or irritation, it’s crucial to respect its boundaries and avoid any further interaction that may escalate the situation. Give your cat space and allow it to calm down before attempting to re-engage.
8.2. Providing Enrichment
If your cat is exhibiting signs of boredom or frustration, providing additional enrichment opportunities can help alleviate these feelings. Interactive toys, scratching posts, and climbing structures can all provide mental and physical stimulation, helping to keep your cat happy and engaged.
8.3. Seeking Professional Help
In some cases, addressing behavioral issues related to tail wagging may require professional help. A veterinarian or certified cat behaviorist can assess your cat’s behavior and provide tailored recommendations for addressing any underlying issues.
9. The Role of Genetics and Breed in Tail Wagging
Genetics and breed can play a significant role in a cat’s tail wagging behavior. Certain breeds may be predisposed to specific tail movements or communication styles. For example, some breeds are known for their expressive tails, while others may be more subtle in their communication.
9.1. Selective Breeding
Selective breeding practices can also influence tail wagging behavior. Breeders may intentionally select for certain tail traits or communication styles, which can become more prevalent in subsequent generations.
9.2. Individual Variation
Despite the influence of genetics and breed, individual variation is still a significant factor. Each cat has its unique personality and communication style, which can impact how it uses its tail to express itself.
10. The Importance of Consistency in Interpretation
Consistency in interpreting cat tail signals is crucial for effective communication and building trust. By consistently responding to your cat’s tail movements in a predictable and appropriate manner, you can help create a strong and secure bond.
10.1. Avoiding Mixed Signals
Avoiding mixed signals is essential for clear communication. If you inconsistently respond to your cat’s tail movements, it can become confused and may struggle to understand your intentions.
10.2. Seeking Expert Guidance
If you’re unsure about how to interpret your cat’s tail signals, seeking guidance from a veterinarian or certified cat behaviorist can be helpful. These professionals can provide personalized advice and support, helping you to better understand your cat’s unique communication style.
11. Recent Research and Studies on Cat Tail Behavior
Recent research and studies have shed new light on the complexities of cat tail behavior. Researchers have used various methods, including video analysis and behavioral experiments, to investigate the relationship between tail movements and emotional states.
11.1. Findings on Tail Asymmetry
One interesting finding is that cats may exhibit tail asymmetry, meaning that they wag their tails more to one side than the other depending on their emotional state. This asymmetry may be related to the lateralization of brain function, with different hemispheres controlling different emotions.
11.2. Influence of Social Context
Studies have also shown that the social context can influence cat tail behavior. Cats may use different tail signals when interacting with familiar individuals compared to strangers.
12. How solcat.net Can Help You Understand Your Cat
At solcat.net, we are dedicated to providing you with the latest information and resources to help you better understand your feline companion. Our website features a wealth of articles, videos, and expert advice on cat behavior, health, and care.
12.1. Comprehensive Resources
We offer comprehensive resources on cat body language, including detailed explanations of different tail signals and their meanings. Our articles are written by experienced veterinarians and cat behaviorists, ensuring that you receive accurate and reliable information.
12.2. Interactive Tools
We also provide interactive tools, such as quizzes and videos, to help you test your knowledge and improve your understanding of cat behavior. Our interactive tools make learning fun and engaging, helping you to retain information more effectively.
12.3. Community Forum
Join our community forum to connect with other cat lovers, share your experiences, and ask questions. Our community forum is a supportive and welcoming space where you can learn from others and share your knowledge.
13. Conclusion: Building a Stronger Bond Through Understanding
Understanding what a cat wagging his tail means is essential for building a stronger bond with your feline friend. By paying attention to their tail movements and other body language cues, you can gain valuable insights into their emotional state and respond accordingly.
Remember, every cat is unique, and individual variation is a significant factor. Take the time to observe your cat’s behavior and learn its specific communication style.
14. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is a cat wagging its tail always a sign of anger?
No, a cat wagging its tail can indicate various emotions, including excitement, focus, or irritation. Context is key to understanding the underlying emotion.
2. What does it mean when a cat’s tail is puffed up?
A puffed-up tail is a clear sign of fear or aggression. The cat is trying to appear larger to ward off a perceived threat.
3. Why does my cat wrap its tail around me?
When a cat wraps its tail around you, it’s a sign of affection and trust. This gesture indicates that your cat feels comfortable and secure in your presence.
4. How can I tell if my cat is happy?
Signs of a happy cat include a relaxed body posture, slow blinking, purring, and rubbing against you.
5. What should I do if my cat is showing signs of fear or anxiety?
If your cat is showing signs of fear or anxiety, provide a safe and calming environment. Avoid forcing interaction and allow your cat to retreat to a quiet space where it feels secure.
6. Can genetics influence a cat’s tail wagging behavior?
Yes, genetics and breed can play a role in a cat’s tail wagging behavior. Certain breeds may be predisposed to specific tail movements or communication styles.
7. Is it essential to consider other body language cues when interpreting cat tail signals?
Yes, it’s essential to consider other body language cues, such as facial expressions, ear positions, and body posture, for a more complete understanding.
8. How can I improve my understanding of cat behavior?
You can improve your understanding of cat behavior by reading books, articles, and websites like solcat.net, observing your cat’s behavior, and consulting with a veterinarian or certified cat behaviorist.
9. What are some common misconceptions about cat tail wagging?
Some common misconceptions include that a wagging tail always indicates happiness and that all wags are the same.
10. When should I seek professional help for my cat’s behavioral issues?
You should seek professional help if your cat is exhibiting persistent behavioral issues, such as aggression, anxiety, or excessive vocalization.
By understanding your cat’s tail wags and body language, you create a deeper connection and a happier life together. Visit solcat.net for more insights and resources to enhance your feline relationship. At Address: 950 Alaskan Way, Seattle, WA 98104, United States or give us a call at Phone: +1 (206) 386-4000.


